数据结构刷题
141.环形链表(简单题)
给你一个链表的头节点 head ,判断链表中是否有环。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递 。仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
如果链表中存在环 ,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
示例1:
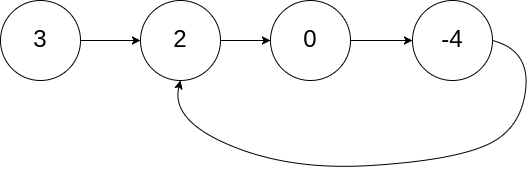
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例2:
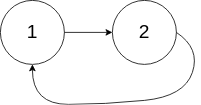
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
实例3:

输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:false
解释:链表中没有环。
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围是
[0, 104] -105 <= Node.val <= 105pos为-1或者链表中的一个 有效索引 。
题解:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
ListNode *slow = head, *fast = head;
while(fast != nullptr && fast->next != nullptr)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if (slow == fast)
return true;
}
return false;
}
};
21.合并两个有序链表(简单题)
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例1:
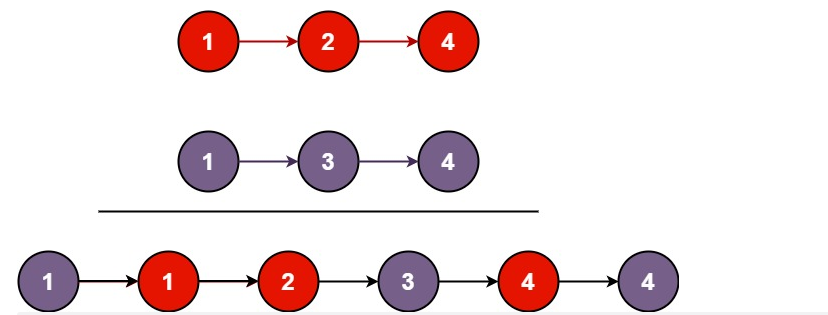
输入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
示例2:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = []
输出:[]
示例3:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = [0]
输出:[0]
提示:
- 两个链表的节点数目范围是
[0, 50] -100 <= Node.val <= 100l1和l2均按 非递减顺序 排列
题解1(暴力):
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {
ListNode *head = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode *tmp = head;
while(list1 != nullptr && list2 != nullptr)
{
if (list1->val < list2->val)
{
tmp->next = list1;
list1 = list1->next;
}
else
{
tmp->next = list2;
list2 = list2->next;
}
tmp = tmp->next;
}
if (list1 == nullptr)
tmp->next = list2;
else
tmp->next = list1;
// tmp->next = list1 == nullptr ? list2 : list1;
return head->next;
}
};
题解2递归:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {
if (list1 == nullptr)
return list2;
if (list2 == nullptr)
return list1;
if (list1->val <= list2->val)
{
list1->next = mergeTwoLists(list1->next, list2);
return list1;
}
else
{
list2->next = mergeTwoLists(list1, list2->next);
return list2;
}
}
};
203.移除链表元素(简单题)
给你一个链表的头节点 head 和一个整数 val ,请你删除链表中所有满足 Node.val == val 的节点,并返回 新的头节点 。
示例1:
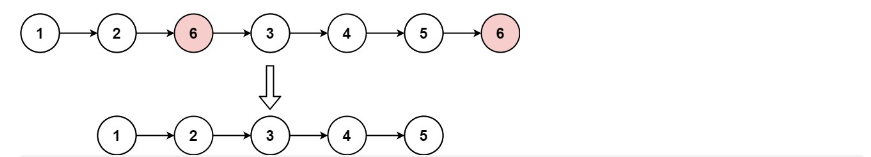
输入:head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6
输出:[1,2,3,4,5]
示例2:
输入:head = [], val = 1
输出:[]
示例3:
输入:head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7
输出:[]
提示:
- 列表中的节点数目在范围
[0, 104]内 1 <= Node.val <= 500 <= val <= 50
题解1(暴力):
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
ListNode *res = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode * tmp = res;
while(nullptr != tmp->next)
{
if (val == tmp->next->val)
{
tmp->next = tmp->next->next;
}
else
{
tmp = tmp->next;
}
}
return res->next;
}
};
题解2(递归):
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
if (head == nullptr) {
return head;
}
head->next = removeElements(head->next, val);
return head->val == val ? head->next : head;
}
};
206.反转链表(简单题)
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例1:
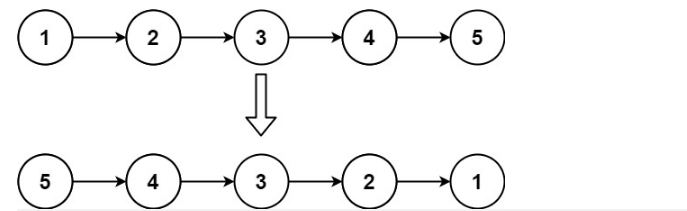
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
示例2:
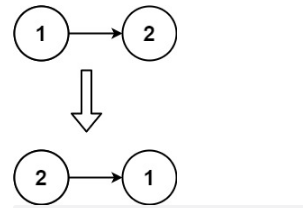
输入:head = [1,2]
输出:[2,1]
示例3:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围是
[0, 5000] -5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
题解1,原地算法:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr)
return head;
ListNode * L = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode * beg = L->next;
ListNode * end = L->next->next;
while(end)
{
beg->next = end->next;
end->next = L->next;
L->next = end;
end = beg->next;
}
return L->next;
}
};
题解2,递归:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr)
return head;
ListNode *newHead = reverseList(head->next);
head->next->next = head;
head->next = nullptr;
/*
第一轮出栈,head为5,head.next为空,返回5
第二轮出栈,head为4,head.next为5,执行head.next.next=head也就是5.next=4,
把当前节点的子节点的子节点指向当前节点
此时链表为1->2->3->4<->5,由于4与5互相指向,所以此处要断开4.next=null
此时链表为1->2->3->4<-5
返回节点5
第三轮出栈,head为3,head.next为4,执行head.next.next=head也就是4.next=3,
此时链表为1->2->3<->4<-5,由于3与4互相指向,所以此处要断开3.next=null
此时链表为1->2->3<-4<-5
返回节点5
第四轮出栈,head为2,head.next为3,执行head.next.next=head也就是3.next=2,
此时链表为1->2<->3<-4<-5,由于2与3互相指向,所以此处要断开2.next=null
此时链表为1->2<-3<-4<-5
返回节点5
第五轮出栈,head为1,head.next为2,执行head.next.next=head也就是2.next=1,
此时链表为1<->2<-3<-4<-5,由于1与2互相指向,所以此处要断开1.next=null
此时链表为1<-2<-3<-4<-5
返回节点5
出栈完成,最终头节点5->4->3->2->1
*/
return newHead;
};
题解3,枚举:
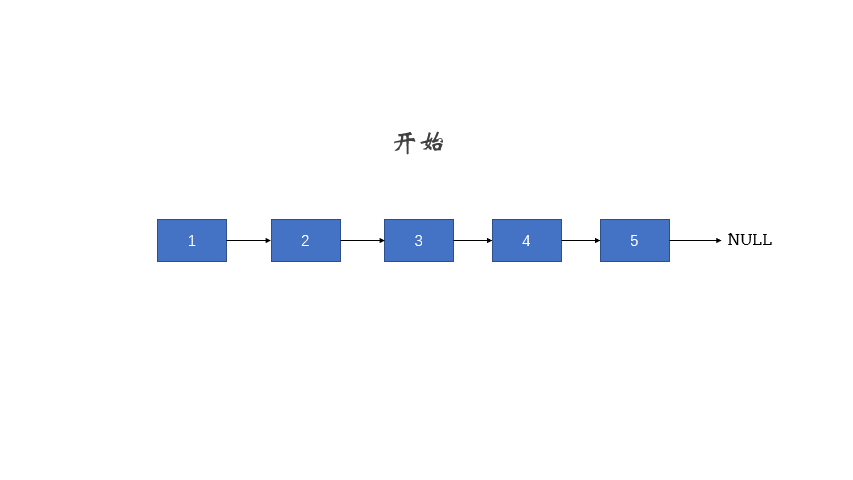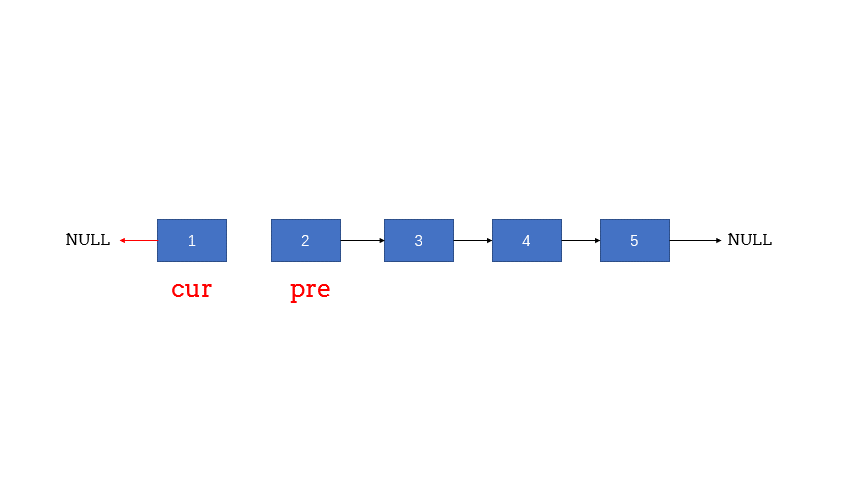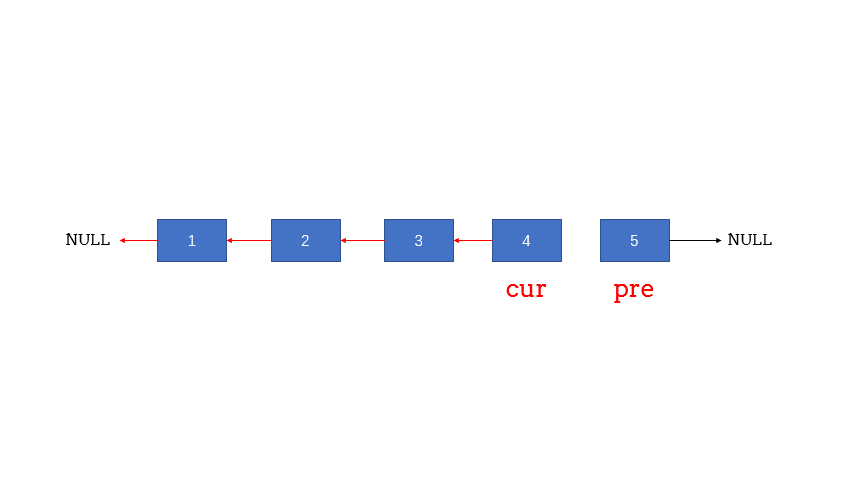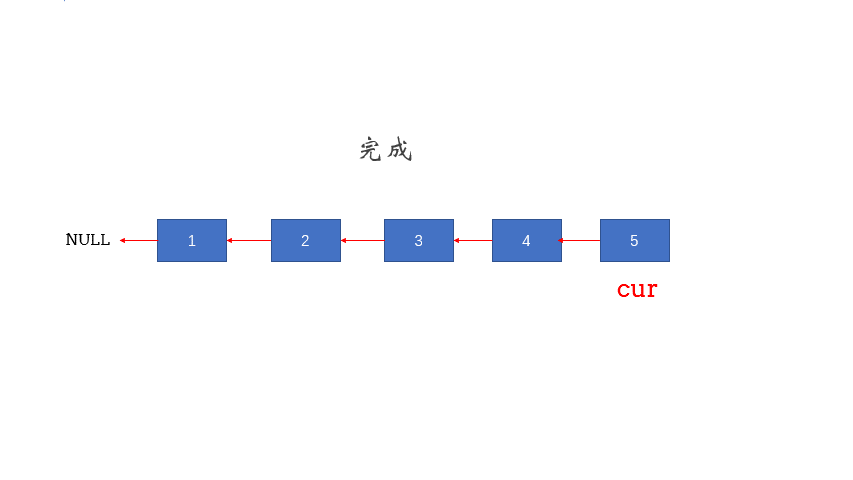
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr)
return haed;
ListNode * cur = nullptr;
ListNode * pre = head;
while(cur != nullptr)
{
ListNode *tmp = pre->next; //临时保存 pre 的 下一节点
pre->next = cur; // 指向掉头
cur = pre; // cur 移动一个位置
pre = tmp; // pre 移动一个位置
}
return cur;
}
};
83.删除排序链表中的重复元素(简单题)
给定一个已排序的链表的头 head , 删除所有重复的元素,使每个元素只出现一次 。返回 已排序的链表 。
示例1:
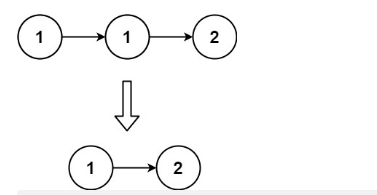
输入:head = [1,1,2]
输出:[1,2]
示例2:
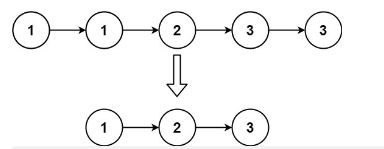
输入:head = [1,1,2,3,3]
输出:[1,2,3]
提示:
- 链表中节点数目在范围
[0, 300]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100- 题目数据保证链表已经按升序 排列
题解1,两个for循环 暴力破解:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr)
return head;
for (ListNode *index = head; index != nullptr; index = index->next)
{
for (ListNode * index2 = index->next; index2 != nullptr; index2 = index2->next)
{
if (index->val == index2->val)
{
index->next = index2->next;
}
else
break;
}
}
return head;
}
};
题解2,一层while循环 枚举:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
ListNode *ptr = head;
while(ptr && ptr->next)
{
if (ptr->val == ptr->next->val)
{
ListNode *del = ptr->next;
ptr->next = del->next;
delete(del);
}
else
ptr = ptr->next;
}
return head;
}
};
题解3,递归:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr)
return head;
head->next = deleteDuplicates(head->next);
if (head->val == head->next->val)
head->next = head->next->next;
return head;
}
};
20.有效的括号(简单题)
给定一个只包括 '(',')','{','}','[',']' 的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
- 左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
- 左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
- 每个右括号都有一个对应的相同类型的左括号。
示例1:
输入:s = "()"
输出:true
示例2:
输入:s = "()[]{}"
输出:true
示例3:
输入:s = "(]"
输出:false
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 104s仅由括号'()[]{}'组成
题解(栈):
class Solution {
public:
bool isValid(string s) {
if (s.length() % 2 == 1)
return false;
unordered_map<char, char> pair = {
{')', '('},
{']', '['},
{'}', '{'}
};
stack<char> stack;
for (auto index : s)
{
if (pair.count(index))
{
if (stack.empty() || stack.top() != pair[index])
return false;
stack.pop();
}
else
stack.push(index);
}
return stack.empty();
}
};
232.用栈实现队列(简单)
请你仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列。队列应当支持一般队列支持的所有操作(push、pop、peek、empty):
实现 MyQueue 类:
void push(int x)将元素x推到队列的末尾int pop()从队列的开头移除并返回元素int peek()返回队列开头的元素boolean empty()如果队列为空,返回true;否则,返回false
说明
- 你 只能 使用标准的栈操作 —— 也就是只有
push to top,peek/pop from top,size, 和is empty操作是合法的 - 你所使用的语言也许不支持栈。你可以使用
list或者deque(双端队列)来模拟一个栈,只要是标准的栈操作即可。
示例1:
输入:
["MyQueue", "push", "push", "peek", "pop", "empty"]
[[], [1], [2], [], [], []]
输出:
[null, null, null, 1, 1, false]
解释:
MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue();
myQueue.push(1); // queue is: [1]
myQueue.push(2); // queue is: [1, 2] (leftmost is front of the queue)
myQueue.peek(); // return 1
myQueue.pop(); // return 1, queue is [2]
myQueue.empty(); // return false
提示
1 <= x <= 9- 最多调用
100次push、pop、peek和empty - 假设所有操作都是有效的 (例如,一个空的队列不会调用
pop或者peek操作)
题解:
class MyQueue {
private:
stack<int> inStack, outStack;
void InToOut()
{
while (!inStack.empty())
{
outStack.push(inStack.top());
inStack.pop();
}
}
public:
MyQueue() {
}
void push(int x) {
inStack.push(x);
}
int pop() {
if (outStack.empty())
InToOut();
int x = outStack.top();
outStack.pop();
return x;
}
int peek() {
if (outStack.empty())
InToOut();
return outStack.top();
}
bool empty() {
return inStack.empty() && outStack.empty();
}
};
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue* obj = new MyQueue();
* obj->push(x);
* int param_2 = obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->peek();
* bool param_4 = obj->empty();
*/
144.二叉树前序遍历(简单题)
给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回它节点值的 前序 遍历
示例1
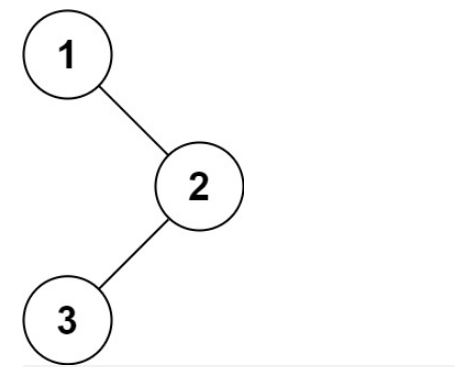
输入:root = [1,null,2,3]
输出:[1,2,3]
示例2
输入:root = []
输出:[]
示例3
输入:root = [1]
输出:[1]
示例4
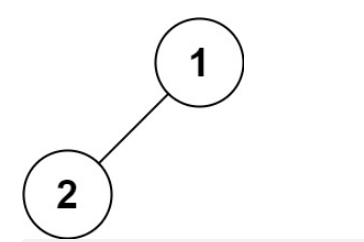
输入:root = [1,2]
输出:[1,2]
示例5
输入:root = [1,null,2]
输出:[1,2]
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[0, 100]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
题解1,递归:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void func(TreeNode * root, vector<int> &res)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return ;
res.push_back(root->val);
func(root->left, res);
func(root->right, res);
}
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
func(root, res);
return res;
}
};
题解2,迭代:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
if (root == nullptr)
return res;
stack<TreeNode* root> stk;
TreeNode* node = root;
while (! stk.empty() || node != nullptr)
{
while(node != nullptr)
{
res.push_back(node->val);
stk.push(node);
node = node->left;
}
node = stk.top();
stk.pop();
node = node->right;
}
return res;
}
};
94.二叉树中序遍历(简单题)
给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回 它的 中序 遍历 。
示例1:
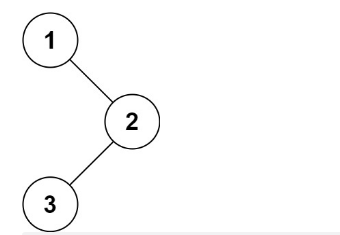
输入:root = [1,null,2,3]
输出:[1,3,2]
示例2:
输入:root = []
输出:[]
示例3:
输入:root = [1]
输出:[1]
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[0, 100]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
题解1,递归:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void func(TreeNode * root, vector<int> &res)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return ;
func(root->left, res);
res.push_back(root->val);
func(root->right, res);
}
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
func(root, res);
return res;
}
};
题解2,迭代:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
if (root == nullptr)
return res;
stack<TreeNode * > stk;
TreeNode * node = root;
while(! stk.empty() || node != nullptr)
{
while(node != nullptr)
{
stk.push(node);
node = node->left;
}
node = stk.top();
stk.pop();
res.push_back(node->val);
node = node->right;
}
return res;
}
};
145.二叉树后续遍历(简单题)
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 后序遍历 。
示例1:
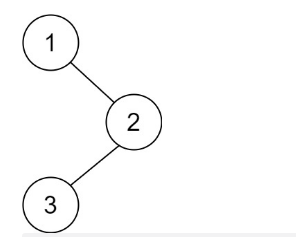
输入:root = [1,null,2,3]
输出:[3,2,1]
示例2:
输入:root = []
输出:[]
示例3:
输入:root = [1]
输出:[1]
提示:
- 树中节点的数目在范围
[0, 100]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
题解1,递归:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
void func(TreeNode* root, vector<int> & res)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return ;
func(root->left, res);
func(root->right, res);
res.push_back(root->val);
}
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
func(root, res);
return res;
}
};
题解2,迭代:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
if (root == nullptr)
return res;
stack<TreeNode *> stk;
TreeNode *node = root;
TreeNode *prev = nullptr;
while(!stk.empty() || node != nullptr)
{
while (node != nullptr)
{
stk.push(node);
node = node->left;
}
node = stk.top();
stk.pop();
if (node->right == nullptr || node->right == prev)
{
res.push_back(node->val);
prev = node;
node = nullptr; //置空防止死循环,且下一次的节点会在栈顶取得
}
else
{
stk.push(node);
node = node->right;
}
}
return res;
}
};
102.二叉树的层序遍历(中等题)
给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 层序遍历 。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。
示例1:
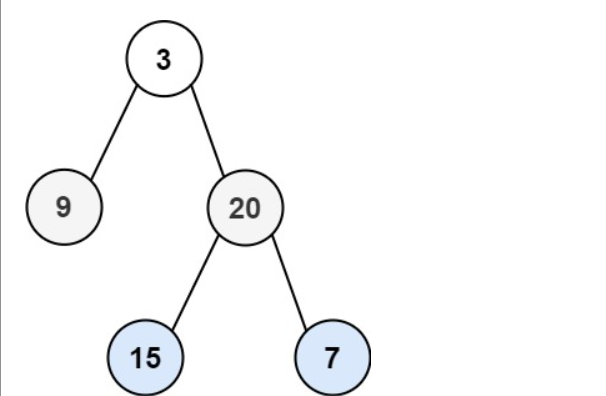
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:[[3],[9,20],[15,7]]
示例2:
输入:root = [1]
输出:[[1]]
示例3:
输入:root = []
输出:[]
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[0, 2000]内 -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
题解1,迭代,BFS:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
if (nullptr == root)
return res;
queue<TreeNode *> que;
que.push(root);
while (! que.empty())
{
vector<int> level;
int levelCount = que.size();
for (int i = 0; i < levelCount; i++) //不能使用que.size 因为que.size 在变化
{
TreeNode *node = que.front();
que.pop();
if (node->left)
que.push(node->left);
if (node->right)
que.push(node->right);
level.push_back(node->val);
}
res.push_back(level);
}
return res;
}
};
104.二叉树的最大深度(简单题)
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例: 给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回它的最大深度 3 。
题解1,递归:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (nullptr == root)
return 0;
return max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right)) + 1;
}
};
题解2,深度优先搜索:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
int res = 0;
if (nullptr == root)
return res;
stack<TreeNode *> nodeStk;
stack<int> depStk;
nodeStk.push(root);
depStk.push(1);
while(! nodeStk.empty())
{
TreeNode *node = nodeStk.top();
nodeStk.pop();
int level = depStk.top();
depStk.pop();
res = max(res, level);
if (node->left)
{
nodeStk.push(node->left);
depStk.push(level + 1);
}
if (node->right)
{
nodeStk.push(node->right);
depStk.push(level + 1);
}
}
return res;
}
};
题解3,广度优先搜索:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
int res = 0;
if (nullptr == root)
return res;
queue<TreeNode *> que;
que.push(root);
while(! que.empty())
{
int size = que.size();
res++;
while (size-- > 0)
{
TreeNode *node = que.front();
que.pop();
if (node->left)
que.push(node->left);
if (node->right)
que.push(node->right);
}
}
return res;
}
};
101.对称二叉树(简单题)
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root , 检查它是否轴对称。
示例 1:
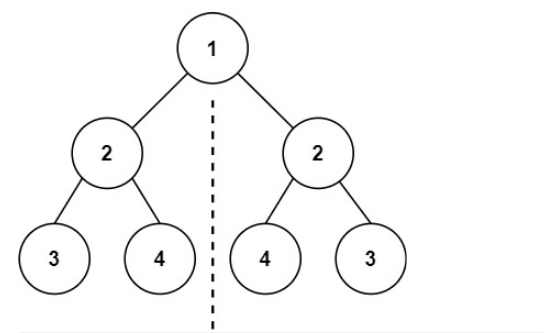
输入:root = [1,2,2,3,4,4,3]
输出:true
示例 2:
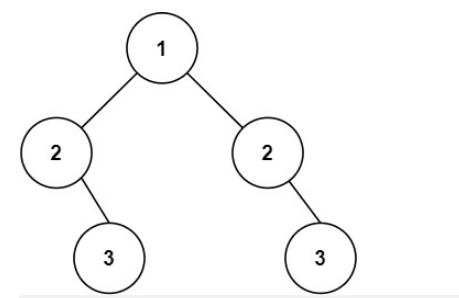
输入:root = [1,2,2,null,3,null,3]
输出:false
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[1, 1000]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
题解1,迭代,BFS:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode *> que;
que.push(root->left);
que.push(root->right);
while(! que.empty())
{
TreeNode * left = que.front();
que.pop();
TreeNode * right = que.front();
que.pop();
if (left == nullptr && right == nullptr)
continue;
if (left == nullptr || right == nullptr)
return false;
if (left->val != right->val)
return false;
que.push(left->left);
que.push(right->right);
que.push(left->right);
que.push(right->left);
}
return true;
}
};
题解2,递归:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
return func(root->left, root->right);
}
private:
bool func(TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right)
{
if (left == nullptr && right == nullptr)
return true;
if (left == nullptr || right == nullptr)
return false;
if (left->val != right->val)
return false;
return func(left->left,right->right) && func(left->right, right->left);
}
};
226.翻转二叉树(简单题)
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,翻转这棵二叉树,并返回其根节点。
示例 1:
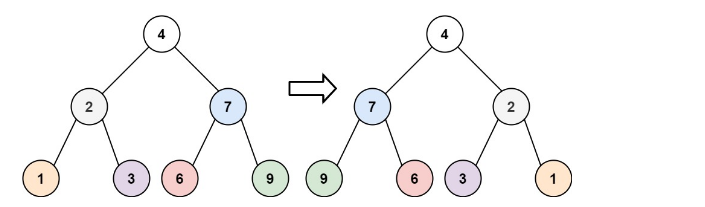
输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9]
输出:[4,7,2,9,6,3,1]
示例 2:
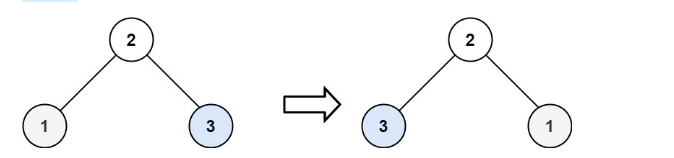
输入:root = [2,1,3]
输出:[2,3,1]
示例 3:
输入:root = []
输出:[]
提示:
- 树中节点数目范围在
[0, 100]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
题解1,迭代,BFS:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if (nullptr == root)
return nullptr;
queue<TreeNode *> que;
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty())
{
int size = que.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
TreeNode *node = que.front();
que.pop();
swap(node->left, node->right);
if (node->left)
que.push(node->left);
if (node->right)
que.push(node->right);
}
}
return root;
}
};
题解2,迭代,DFS:
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if (nullptr == root)
return nullptr;
stack<TreeNode *> stk;
stk.push(root);
while(!stk.empty())
{
TreeNode * node = stk.top();
stk.pop();
swap(node->left, node->right);
if (node->left)
stk.push(node->left);
if (node->right)
stk.push(node->right);
}
return root;
}
};
题解3,递归:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if (nullptr == root)
return nullptr;
swap(root->left, root->right);
invertTree(root->left);
invertTree(root->right);
return root;
}
};
112.路径总和(简单题)
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个表示目标和的整数 targetSum 。判断该树中是否存在 根节点到叶子节点 的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和 targetSum 。如果存在,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
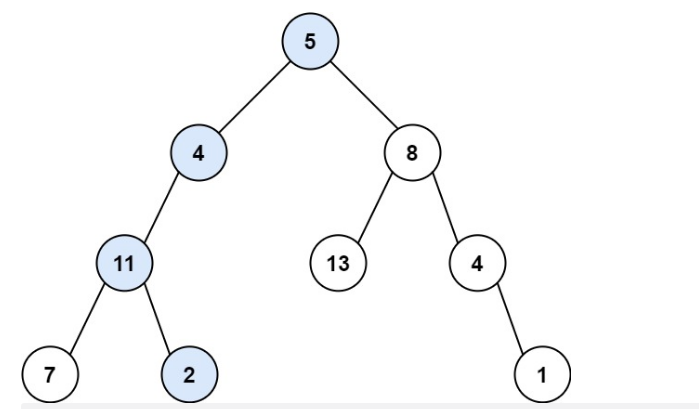
输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1], targetSum = 22
输出:true
解释:等于目标和的根节点到叶节点路径如上图所示。
示例 2:
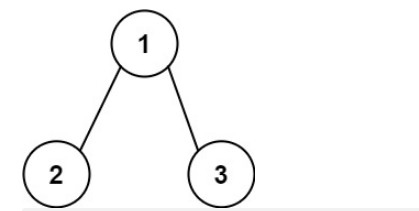
输入:root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5
输出:false
解释:树中存在两条根节点到叶子节点的路径:
(1 --> 2): 和为 3
(1 --> 3): 和为 4
不存在 sum = 5 的根节点到叶子节点的路径。
示例 3:
输入:root = [], targetSum = 0
输出:false
解释:由于树是空的,所以不存在根节点到叶子节点的路径。
提示:
- 树中节点的数目在范围
[0, 5000]内 -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
题解1,递归:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if (!root)
return false;
if (!root->left && !root->right && targetSum == root->val)
return true;
return hasPathSum(root->left, targetSum - root->val) || hasPathSum(root->right, targetSum - root->val);
}
};
题解2,BFS:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if (nullptr == root)
return false;
queue<TreeNode *> queNode;
queue<int> queRes;
queNode.push(root);
queRes.push(root->val);
while(!queNode.empty())
{
TreeNode *node = queNode.front();
queNode.pop();
int tmp = queRes.front();
queRes.pop();
if (tmp == targetSum && nullptr == node->left && nullptr == node->right)
return true;
if (node->left)
{
queNode.push(node->left);
queRes.push(node->left->val + tmp);
}
if (node->right)
{
queNode.push(node->right);
queRes.push(node->right->val + tmp);
}
}
return false;
}
};
700.二叉搜索树中的搜索(简单题)
给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点 root 和一个整数值 val。
你需要在 BST 中找到节点值等于val的节点。 返回以该节点为根的子树。 如果节点不存在,则返回null 。
示例1:
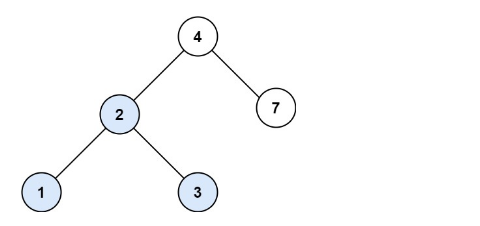
输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3], val = 2
输出:[2,1,3]
示例2:
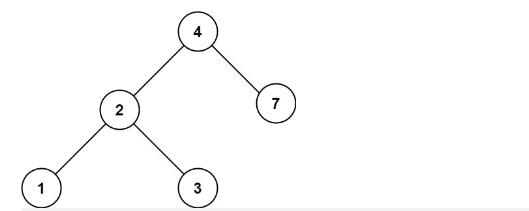
输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3], val = 5
输出:[]
提示:
- 数中节点数在
[1, 5000]范围内 1 <= Node.val <= 107root是二叉搜索树1 <= val <= 107
题解1,迭代:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* searchBST(TreeNode* root, int val) {
while(root)
{
if (root->val == val)
return root;
root = root->val > val ? root->left : root->right;
}
return nullptr;
}
};
题解2,递归:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* searchBST(TreeNode* root, int val) {
if (nullptr == root)
return nullptr;
if (root->val == val)
return root;
return searchBST(root->val > val ? root->left : root->right, val);
}
};
701. 二叉搜索树中的插入操作(中等题)
给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点 root 和要插入树中的值 value ,将值插入二叉搜索树。 返回插入后二叉搜索树的根节点。 输入数据 保证 ,新值和原始二叉搜索树中的任意节点值都不同。
注意,可能存在多种有效的插入方式,只要树在插入后仍保持为二叉搜索树即可。 你可以返回 任意有效的结果 。
示例1:
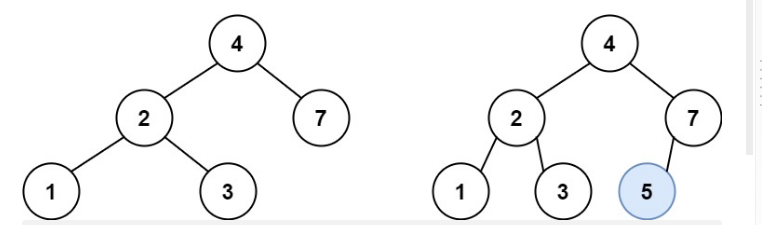
输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3], val = 5
输出:[4,2,7,1,3,5]
解释:另一个满足题目要求可以通过的树是:
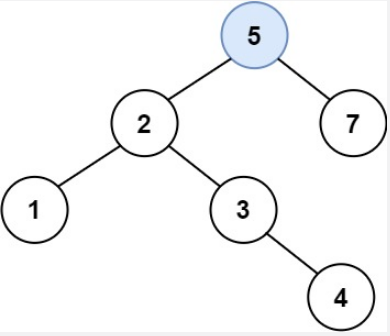
示例 2:
输入:root = [40,20,60,10,30,50,70], val = 25
输出:[40,20,60,10,30,50,70,null,null,25]
示例 3:
输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3,null,null,null,null,null,null], val = 5
输出:[4,2,7,1,3,5]
题解1,迭代:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* insertIntoBST(TreeNode* root, int val) {
if (!root)
{
return new TreeNode(val);
}
TreeNode *index = new TreeNode(val);
TreeNode *node = root;
while (node)
{
if (node->val > val)
{
if (nullptr == node->left)
{
node->left = index;
break;
}
else
node = node->left;
}
else
{
if (nullptr == node->right)
{
node->right = index;
break;
}
else
node = node->right;
}
}
return root;
}
};
题解2,递归:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* insertIntoBST(TreeNode* root, int val) {
if (nullptr == root)
return new TreeNode(val);
if (root->val < val)
root->right = insertIntoBST(root->right, val);
else
root->left = insertIntoBST(root->left, val);
return root;
}
};
98.验证二叉搜索树(中等题)
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。
有效 二叉搜索树定义如下:
- 节点的左子树只包含 小于 当前节点的数。
- 节点的右子树只包含 大于 当前节点的数。
- 所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树。
示例 1:
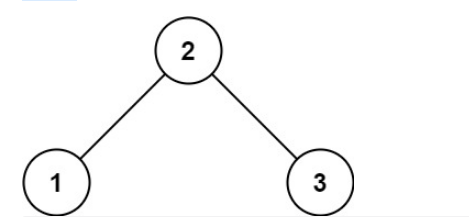
输入:root = [2,1,3]
输出:true
输入:root = [5,1,4,null,null,3,6]
输出:false
解释:根节点的值是 5 ,但是右子节点的值是 4 。
提示:
- 树中节点数目范围在
[1, 104]内 -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
题解1: